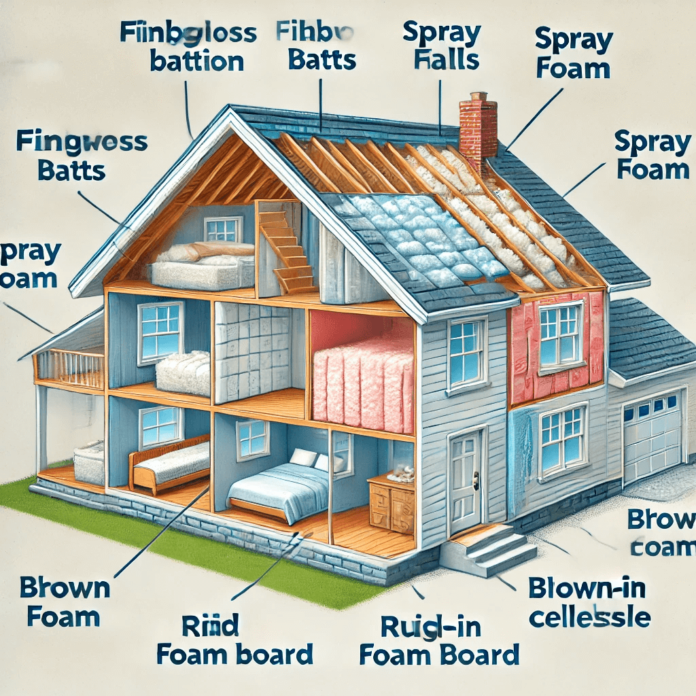
Introduction
A well-insulated home improves energy efficiency, reduces utility costs, and enhances overall comfort. This home insulation guide explores different types of insulation and their specific advantages. From fiberglass and spray foam to cellulose and rigid foam, choosing the right insulation ensures better temperature regulation year-round. Understanding insulation benefits, such as noise reduction, moisture control, and lower energy consumption, can help homeowners make informed decisions. Let’s dive into the best insulation options for your home and how they contribute to a more sustainable and comfortable living environment.
Home insulation is a cornerstone of energy efficiency, comfort, and sustainability. With energy costs rising globally and climate goals tightening, understanding insulation types, benefits, and installation best practices is critical. This guide synthesizes insights from industry reports, cost analyses, and technical studies to help homeowners make informed decisions.
1. Types of Home Insulation
A. Loft and Roof Insulation
Heat escapes most readily through uninsulated roofs, accounting for 26% of home heat loss. Key options include:
- Pitched Roofs: Insulation is placed between rafters or under slopes. Materials like PIR boards (high R-value of 6.0–8.0 per inch) or mineral wool are ideal for cold climates.
- Flat Roofs: Often insulated with rigid foam boards (e.g., PIR) or spray foam to resist moisture and heat transfer.
- Loft Insulation: Cost-effective and quick to install, with savings of £270–£475/year depending on home type and region. Payback periods average 3 years.
B. Wall Insulation
- Cavity Walls: Found in post-1920 homes, insulation is injected into gaps. Costs £2,700–£12,000 and reduces heat loss by 35%.
- Solid Walls: Common in pre-1920 homes. Internal insulation (cheaper but reduces room space) or external cladding (costly but durable) can save £380/year.
- Materials: Fiberglass batts (£0.80–£2.60/sq. ft.) or spray foam (closed-cell for moisture resistance, R-5–7 per inch).
C. Floor Insulation
A comparison insulation between timber vs. concrete can help homeowners decide on the best material for energy efficiency, durability, and insulation performance.
- Suspended Timber Floors: Insulate with mineral wool between joists, saving £80/year.
- Concrete Floors: Use rigid foam boards (e.g., XPS polystyrene) to reduce heat loss by 8%.
D. Windows and Doors
Double-glazed windows cut heat loss by 30% while draught-proofing gaps with adhesive strips or excluders saves £165–£210/year.
E. Pipes and Water Tanks
Insulating pipes and radiators reduces heat loss by 12%. Reflector panels behind radiators and hot water cylinder jackets are cost-effective upgrades.
2. Key Benefits of Home Insulation
A. Energy and Cost Savings
- Annual Savings: Loft insulation saves £200–£475, cavity walls £255–£380, and floors £80.
- Reduced HVAC Strain: Proper insulation lowers heating/cooling energy use by 15–50%, extending the HVAC lifespan.
B. Environmental Impact
- CO2 Reduction: A well-insulated home cuts annual emissions by 0.6–1.7 tonnes, aiding the UK’s 2050 net-zero target.
- Resource Conservation: Insulation reduces fossil fuel dependency and water use in energy production.
C. Comfort and Health
- Temperature Stability: Eliminates drafts and maintains consistent indoor temperatures year-round.
- Mold Prevention: Reduces condensation and dampness, lowering respiratory risks.
D. Property Value
Homes with high EPC ratings (achieved through insulation) see value increases of up to 14%.
3. Best Practices for Installation
A. Choose the Right Material
Climate Considerations:
- Cold Climates: Prioritize high R-value materials like spray foam (R-6–7 per inch) or PIR boards.
- Hot Climates: Reflective insulation (e.g., radiant barriers) blocks solar heat gain.
- Eco-Friendly Insulation Options: Sheep’s wool (R-3.5–4.5) or cellulose (recycled paper) for sustainability.
B. Professional vs. DIY Installation
- DIY-Friendly: Fiberglass batts (£0.30–£1.30/sq. ft.) or loose-fill cellulose.
- Professional Required: Spray foam and rigid boards demand expertise to avoid gaps and ensure safety.
C. Address Structural Needs
- Seal Gaps: Air leaks can negate 30% of insulation’s effectiveness. Use caulk or spray foam around windows and pipes.
- Ventilation: Prevent moisture buildup in lofts with soffit vents or breathable membranes.
D. Leverage Government Incentives
- Great British Insulation Scheme (GBIS): Covers up to 100% of costs for low-income households.
- Energy Company Obligation (ECO): Funds insulation upgrades through energy suppliers.
4. Cost Breakdown and ROI
| Insulation Type | Cost Range (UK) | Annual Savings | Payback Period | |
| Loft | £740–£1,700 | £200–£475 | 3–5 years | |
| Cavity Wall | £2,700–£12,000 | £255–£380 | 7–10 years | |
| Solid Wall | £7,500–£15,000 | £380 | 10–15 years | |
| Floor | £4,700 | £80 | 5–8 years | |
| Spray Foam (Roof) | £55–£70/m² | Varies by R-value | 5–12 years |
5. Future Trends and Innovations
- Smart Insulation: AI-driven systems monitor efficiency and predict maintenance needs.
- Recyclable Materials: Cork and wood fiber boards gain traction for low environmental impact.
- Aerogel: Ultra-thin, high R-value (R-10+ per inch) but costly (£3–£6.50/sq. ft.).
Home Insulation Guide: Everything You Need to Know

Proper insulation is essential for maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient home. This home insulation guide covers the different types of insulation available and how they help improve your living space.
Why Home Insulation Matters
- Energy Efficiency: Reduces heat loss in winter and keeps your home cooler in summer.
- Lower Utility Bills: Proper insulation decreases energy consumption, saving money in the long run.
- Enhanced Comfort: Helps maintain consistent indoor temperatures throughout the year.
- Noise Reduction: Acts as a barrier to minimize outside noise for a quieter home.
Conclusion
A well-insulated home enhances energy efficiency, reduces utility costs, and improves overall comfort. By understanding different insulation types and their benefits, homeowners can make informed choices for a sustainable and cozy living environment. Proper insulation not only regulates indoor temperatures but also minimizes noise and moisture issues. Investing in the right insulation ensures long-term savings and a more comfortable home year-round.
Home insulation is a strategic investment that pays dividends in energy savings, comfort, and environmental stewardship. By selecting the right materials, leveraging incentives, and adhering to best practices, homeowners can future-proof their properties against rising energy costs and climate challenges. For personalized quotes or deeper insights, consult resources like GreenMatch UK or the Energy Saving Trust.